Modern design values precision, craftsmanship, and the seamless blending of form with function. Modern plastering techniques for premium residential interiors embody these principles, offering smooth surfaces, durable finishes, and architectural expression that elevate contemporary living spaces.
The success of plastering today lies not only in the skill of application but also in material science and design awareness. Homeowners and designers are increasingly appreciating how versatile plastering can define a home’s visual and structural quality.
While plaster is typically associated with interiors, innovations have also advanced in outdoor plaster, demonstrating how adaptability and craftsmanship combine across both environments.
The Evolution of Plastering in Residential Design
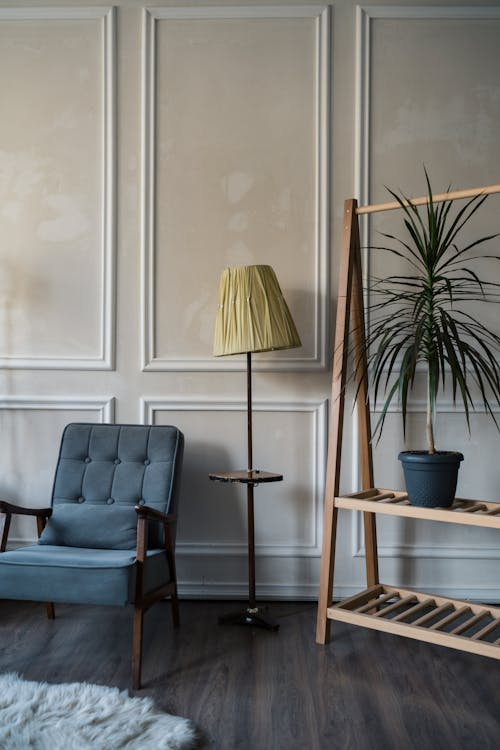

Plaster has been used for centuries, yet modern applications have refined its purpose, extending beyond basic wall finishes into bespoke design features.
From Traditional to Contemporary Application
Historically, plastering relied on lime and sand mixtures applied by hand to create textured surfaces or ornate detailing. Today’s techniques incorporate improved materials and machinery that enhance precision while maintaining the artistry of the trade. Modern plastering provides the flexibility to achieve everything from crisp minimalist walls to complex architectural mouldings.
The Role of Plaster in Modern Interiors
Plastering does more than conceal imperfections—it defines how light interacts with a space. Smooth finishes reflect light evenly, while textured plasters introduce warmth and depth. In premium homes, plastering complements materials like stone, timber, and glass, bridging the gap between traditional craftsmanship and contemporary aesthetics.
Materials That Define Modern Plastering
Advancements in materials have transformed plastering into a precise, performance-driven process.
Gypsum-Based Plaster
Gypsum remains the most common choice for interior finishes due to its versatility and ease of use. It provides a fine, smooth surface suitable for painting and decorative coatings. Its quick setting time and consistency make it ideal for residential interiors where time efficiency and finish quality are essential.
Lime Plaster for Breathability
Lime plaster continues to be used in projects where natural ventilation and flexibility are priorities. Its ability to absorb and release moisture makes it suitable for both new homes and renovations. Lime-based materials reduce cracking and offer a natural, soft sheen prized in high-end interiors.
Cement and Polymer-Modified Plaster
Cement plasters are valued for strength and moisture resistance, particularly in kitchens, bathrooms, and exterior applications. Polymer-modified variations add flexibility and adhesion, supporting smooth finishes even on challenging substrates. In combination with outdoor plaster systems, these materials maintain consistency between internal and external surfaces.
Decorative and Specialty Plasters
Polished plaster, microcement, and Venetian finishes provide depth and texture that standard paint cannot achieve. These materials require specialist application techniques, delivering bespoke results ideal for feature walls or statement ceilings.
The Process of Achieving Premium Finishes
Every plastering project follows a sequence that determines the quality of the final result.
Surface Preparation
Proper preparation begins with cleaning and priming the substrate. Any dust, loose material, or uneven patches are removed to ensure adhesion. Skilled plasterers assess surface stability and apply bonding agents where necessary to prevent delamination.
Layering and Levelling
Modern plastering typically involves multiple layers, each serving a structural or aesthetic purpose. The base coat provides stability, while subsequent coats refine the surface. Each layer is allowed to set before the next is applied, ensuring uniform strength. Mechanical application tools such as spray systems are now commonly used for even distribution, especially in large-scale residential projects.
Finishing and Polishing
The finishing coat defines the overall appearance. Depending on the desired style, plasterers may create a matte, satin, or polished sheen. Fine trowelling, water polishing, or buffing techniques produce a flawless surface ready for paint or decorative treatment. Attention to detail during this phase separates standard work from premium finishes.
Advanced Techniques in Modern Plastering
Contemporary projects benefit from technical innovations that improve speed, consistency, and visual impact.
Skim Coating for Seamless Surfaces
Skim coating remains one of the most effective ways to achieve a perfect finish. It involves applying a thin layer of fine plaster over existing surfaces, concealing imperfections and joints. Modern compounds allow for faster curing and minimal shrinkage, making them ideal for large homes requiring consistent finishes across multiple rooms.
Spray Application Systems
Spray-applied plaster systems provide efficiency without compromising quality. Machines mix and apply plaster uniformly, reducing waste and ensuring consistent thickness. This approach is especially beneficial in projects with expansive wall and ceiling areas where precision is paramount.
Lightweight and Fibre-Reinforced Plaster
Modern formulations include fibres that enhance strength and flexibility. These prevent cracking and improve durability, particularly in homes experiencing minor structural movement. Lightweight versions reduce pressure on walls and ceilings, supporting energy-efficient design through reduced material use.
Acoustic and Thermal Solutions
Specialty plasters enhance acoustic comfort and thermal efficiency. Sound-absorbing materials are integrated into ceilings and walls to reduce echo, while thermal plasters help maintain indoor temperature. These systems combine functionality with visual elegance, contributing to a refined living experience.
Integrating Design and Functionality
Premium residential interiors demand harmony between craftsmanship and architectural intent.
Collaboration Between Designers and Tradespeople
Plasterers work closely with architects and interior designers to ensure surfaces complement lighting, colour, and form. Early involvement in the design phase helps prevent conflicts between material choices and structural requirements. The result is a cohesive aesthetic where plastering accentuates architectural features.
Creating Architectural Features
Modern plastering extends beyond flat surfaces. Recessed ceilings, curved walls, and integrated lighting troughs showcase how plaster can shape space. Skilled tradespeople craft these forms using precision frameworks and flexible materials, maintaining alignment with design proportions.
Colour and Texture as Design Elements
Pigmented and textured plasters create depth and visual interest without additional finishes. Subtle tones inspired by natural minerals bring warmth and sophistication to interior spaces. These techniques are particularly effective in premium living areas where understated elegance is preferred.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Sustainable construction has become integral to high-end residential projects. Plastering methods now prioritise efficiency, waste reduction, and eco-friendly materials.
Eco-Friendly Materials
Lime, clay, and recycled gypsum products reduce environmental impact. These materials are naturally sourced and contribute to healthy indoor air quality by regulating humidity. Sustainable plastering aligns with green building standards, offering both environmental and lifestyle benefits.
Waste Reduction and Recycling
Mechanical mixing and accurate measurement reduce excess waste. Unused plaster can be recycled or repurposed for future projects. Many modern manufacturers now provide reclaimable systems that transform waste plaster into new material.
Energy Efficiency
Plaster contributes to energy efficiency by improving thermal insulation and sealing. Breathable materials regulate temperature and humidity, reducing the need for artificial climate control. Combined with outdoor plaster applications, this consistency ensures long-term comfort and reduced energy costs.
Challenges in Premium Residential Plastering
Achieving flawless finishes requires attention to environmental and structural factors.
Controlling Moisture and Humidity
Moisture remains one of the most common challenges in plastering. Excess humidity can delay curing or cause bubbling. Skilled tradespeople manage environmental conditions through controlled ventilation and drying schedules, ensuring consistent results.
Managing Temperature Fluctuations
Extreme temperature variations affect plaster setting. Modern compounds include additives that stabilise curing in changing climates, allowing work to proceed year-round without compromising quality.
Coordination with Other Trades
Electrical, plumbing, and HVAC installations often overlap with plastering schedules. Clear communication ensures surfaces remain undamaged during subsequent construction stages. Efficient sequencing between trades reduces delays and prevents costly rework.
Maintaining Quality Over Time
Once installed, plaster finishes require minimal maintenance but benefit from proper care to preserve their longevity.
Cleaning and Repair
Plastered surfaces should be cleaned with mild solutions to prevent damage to coatings. Minor cracks can be filled using fine joint compounds, while larger repairs may require professional refinishing to maintain consistency.
Protection and Longevity
Applying breathable sealants or finishes extends the life of plaster. These treatments protect against moisture while allowing the surface to retain its natural qualities. Regular inspection ensures any early signs of wear are addressed before deterioration occurs.
Adapting to Future Modifications
Modern plastering techniques allow for future updates, such as integrating new lighting or decorative elements. Flexible materials and skilled craftsmanship make modifications easier without compromising structural integrity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of plaster is best for premium residential interiors?
Gypsum plaster is the most common choice due to its smooth texture and versatility. Lime plaster is also used in premium projects for its natural appearance and breathability.
Can modern plastering be used in outdoor areas?
Yes. Specially formulated outdoor plaster systems withstand moisture, temperature changes, and UV exposure. These products ensure durability while maintaining aesthetic harmony between interior and exterior surfaces.
How long does modern plaster last?
With proper installation and care, modern plaster finishes can last for decades. Regular cleaning and controlled humidity help maintain their appearance and structural strength.
Conclusion
Modern plastering techniques for premium residential interiors demonstrate how craftsmanship, innovation, and design collaboration can transform living spaces. From precise skim coats to decorative textures, every stage of the process reflects expertise and attention to detail.
Advances in material technology have expanded plaster’s role beyond surface finishing into a vital component of sustainable and aesthetic design. Whether defining minimalist interiors or blending with outdoor plaster applications, modern plastering remains an essential trade that combines tradition with contemporary excellence, ensuring homes achieve both beauty and long-lasting performance.



Leave a Reply